Pearled Barley: The power of barley to turn a staple food into a healthier food.

Hakubaku history is based on developing and popularizing delicious and easy-to-eat barley rice- and this would not be an overstatement. Barley is packed with nutrients such as calcium, iron and fiber.
Hakubaku made it easy to cook barley with white rice by removing the black crease running down the center of each barley grain.
Hakubaku has developed a range of original products such as white-as-rice polished barley, polished barley with the germ remaining, and Mochimugi, waxy barley. Mochi Mugi Japanese Pearled Barley has 25x times the dietary fiber as white rice, 4 times that of brown rice and 1.5 times that of conventional barley.
Hakubaku continues to develop new products in our bid to promote simple, healthy and good eating for all.
 Since its foundation, Hakubaku has been committed to develop and popularize tasty and easy-to-eat barley rice. Barley was a must-have item for Japanese diet to mix with white rice since 1920’s when Hakubaku was established.
Since its foundation, Hakubaku has been committed to develop and popularize tasty and easy-to-eat barley rice. Barley was a must-have item for Japanese diet to mix with white rice since 1920’s when Hakubaku was established.
It was a important part of many staple foods complementing white rice. As history shows us, barley was not used as a first choice. Demand for barley was prompted by the shortage of the supply of white rice . Barley was used to extend white rice; and a new eating trend began.
White rice is good in nutrition, but nutritional value of barley significantly exceeds white rice. Barley is a nutrient-rich ingredient containing 3 times more of calcium, 2 times more of iron and 17 times more of dietary fibers compared to white rice. Adding barley, as Japanese found out, boosts the nutritional value of white rice.
Need more than 2 bags? We have casepacks ready to ship today!
Barley: Rich in Fiber
Eating barley comes with important health benefits due to the high fiber content. Barley is rich in both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Dietary fiber is a generic term for the material in vegetables, fruits, marine plants and mushrooms that is not broken down by human digestive enzymes.
 Dietary fiber is divided into two main groups. Soluble fiber, which dissolves in water, and insoluble fiber, which does not. It is said that we lack especially soluble fibers as food in general contains 4 times more insoluble fiber than soluble fiber. There is not many food as barley with high content of both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Dietary fiber is divided into two main groups. Soluble fiber, which dissolves in water, and insoluble fiber, which does not. It is said that we lack especially soluble fibers as food in general contains 4 times more insoluble fiber than soluble fiber. There is not many food as barley with high content of both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Insoluble fiber absorbs water and expands, activating the large intestine and stimulating bowel movement. It also expels toxins and gas with stool, keeping your digestive system in good condition.
Soluble fiber is food for the bacteria in your large intestine, such as “lactic acid bacteria” and “Bifidobacterium”. When lactic acid bacteria and Bifidobacterium increase, the influence of gut flora that produces toxins and gas weakens and diminishes, therefore improving the condition of your digestive system.
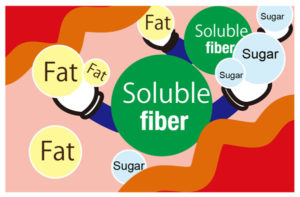
Soluble fiber surrounds sugars and fats, hampering them from being broken down in the small intestine by digestive enzymes. Sugars and fats cannot be absorbed unless they are broken down, which means that the amount of sugars and fats absorbed is reduced. In this way soluble fiber helps regulate blood sugar and cholesterol.
Together both types of fiber work to reduce the risk of coronary heart disease and help improve your overall health.
